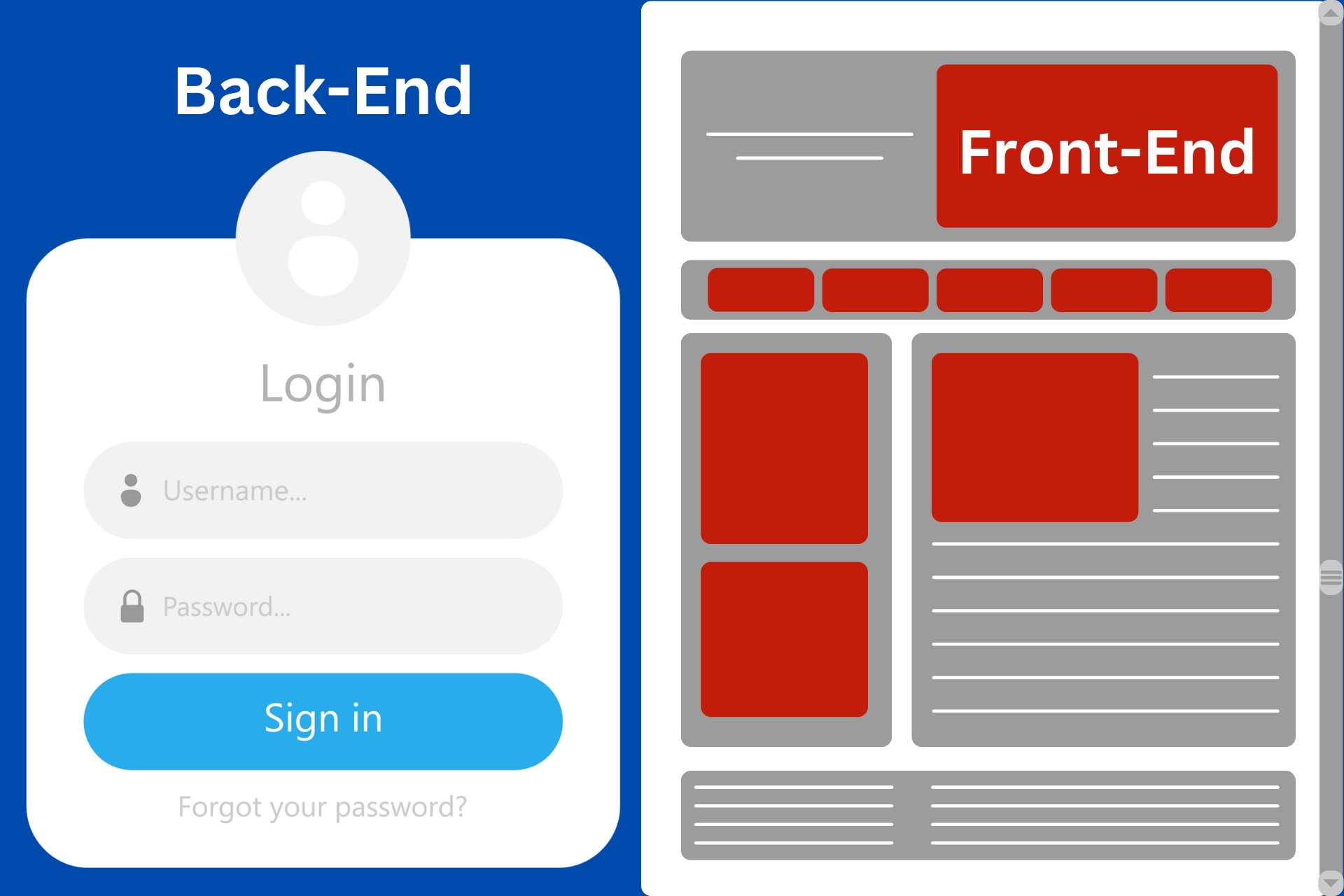
What Is Difference Between Front-end And Back-end System?
Facebook marketing has significantly transformed businesses worldwide by leveraging its extensive reach, advanced targeting capabilities, and a variety of marketing tools. Here are some of the key ways in which Facebook marketing is making an impact:
The front-end and back-end are two crucial components of web development, each serving distinct purposes and functionalities within a web application. Here's a detailed comparison:
Front-End
Definition:
The front-end is the part of a web application that users interact with directly. It includes everything that users experience visually in their browser or application interface.
Key Components:
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): The structure of web pages.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): The styling and layout of web pages.
- JavaScript: The scripting language for creating dynamic and interactive web pages.
- Frameworks/Libraries: Tools like React, Angular, Vue.js that streamline development processes and enhance functionalities.
Responsibilities:
- User Interface (UI): Designing and implementing the layout, look, and feel of the website.
- User Experience (UX): Ensuring the site is easy to navigate and provides a positive experience.
- Responsive Design: Making sure the application works on various devices and screen sizes.
- Interactivity: Handling user inputs and interactions, such as form submissions, button clicks, and animations.
Tools and Technologies:
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Front-end frameworks (e.g., React, Angular, Vue.js)
- CSS preprocessors (e.g., SASS, LESS)
- Build tools (e.g., Webpack, Gulp)
- Version control systems (e.g., Git)
Back-End
Definition:
The back-end is the server side of a web application. It manages the data and logic that power the front-end, ensuring everything works correctly behind the scenes.
Key Components:
- Server: The hardware or virtual machine that hosts the application.
- Database: Where data is stored, retrieved, and managed (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB).
- Server-Side Languages: Programming languages used to build the logic of the application (e.g., Python, Java, Ruby, PHP, Node.js).
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Mechanisms that allow the front-end to communicate with the back-end.
Responsibilities:
- Data Management: Handling database operations such as creating, reading, updating, and deleting data.
- Authentication and Authorization: Managing user authentication (logging in) and authorization (permissions).
- Business Logic: Implementing the core logic of the application, such as calculations, data processing, and decision-making.
- Server Configuration: Setting up and maintaining the server environment.
Tools and Technologies:
- Server-side languages (e.g., Python, Java, PHP, Node.js)
- Databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB)
- Web servers (e.g., Apache, Nginx)
- Frameworks (e.g., Django for Python, Spring for Java, Express for Node.js)
- Version control systems (e.g., Git)
- Containerization and orchestration tools (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes)
Interaction Between Front-End and Back-End
- APIs and AJAX: The front-end interacts with the back-end through APIs, often using AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) to send and receive data without reloading the page.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Communication between the front-end and back-end typically happens over HTTP or HTTPS protocols.
- Data Formats: Data is often exchanged in formats like JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or XML.
Summary
- Front-End: Focuses on the user interface and experience, using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Back-End: Focuses on server-side logic, databases, and application functionality, using technologies like server-side languages, databases, and server frameworks.
Both front-end and back-end development are essential for creating a functional and efficient web application, each with its specialized tools and roles.



Share Link
Or copy link